Advance NMAP Scanning Techniques in 2025

Last updated: July 07, 2025
Nmap: The Network Mapper, used for Discovering live hosts, Scanning open ports, and Identifying Vulnerabilities.
This is PART-2 of the NMAP Tutorial, Read PART-1: The Ultimate Nmap tutorial for Beginners in 2025.
Controlling Speed
Nmap scans are high-speed which makes too much noise in the network and sometimes the firewall blocks it, So for this reason:
- -T<0–5>
0 is the slowest scan and 5 is the fastest scan, Now there is a question why we need 5 as the fastest scan, Sometimes, the fastest scan can bypass the firewall but remember one thing -T5 does not give accurate results! For example:
nmap -sS -p 23,40,80 -T0 <ip-address>
As -T0 is the slowest scan it will take time for the result, Be patient!
Note: You can press the space bar to see how much the scan has been completed.
Changing TCP Flag
You can change the TCP Flags of the packet sent, This helps to bypass the Firewall and provide more accurate results:
Null Scan
- -sN
This sets the Flag to Null means that no flag is set due to this the target machine does not generate any response the lack of response tells us that either the port is open or the Firewall is blocking, For example:
nmap -sN -p 1-1024 <ip-address>
Finish Scan
- -sF
This sets the Flag to Finish means that the Connection that was established before now comes to an end, now the Host machine wants to finish the connection (end). For example:
nmap -sN -p 1-2000 <ip-address>
Xmas Scan
- -sX
This sets the Flag to FIN, PSH, and URG means to finish, push, and urgent respectively. For example:
nmap -sX -p 1-65535 <ip-address>
Ack Scan
- -sA
This is a Different Scan from others. Yeah, it can scan ports, but it is usually used to check if the Firewall is stateful or stateless. A Stateful firewall tracks the Connection established, while a stateless firewall does not. But how is this scan helpful for finding out?
-sA uses the ACK flag, But remember the TCP three-way handshake ACK flag packet is only sent when already SYN flag is sent,
So By sending an ACK flag if it works and shows the open or closed ports, it means there is no firewall or if there is a firewall then it is Stateless Because a stateless firewall does not track the connection and the packet that we have sent with an ACK flag set there was no connection established prior,
So this identifies that if there is a firewall then it is stateless! For example:
nmap -sA -p 1-2000 <ip-address>
TCP Windows Scan
- -sW
This scan works by examining the TCP window Field of the RST packet, If the port is really closed then the window size will be Zero on RST packet. For example:
nmap -sW -p 1-1023 <ip-address>
TCP Maimon Scan
- -sM
This scan works the same as FIN, NULL, and Xmas scans except the packet sent is FIN/ACK Flag. For example:
nmap -sM -p 22,80,443 <ip-address>
Custom TCP Scan
- — scanflags <RST SYN FIN ACK>
This command allows you to customize TCP packets with different types of flags but remember when using more than one flag there will be no space, For example:
nmap --scanflags FINACK -p 1-2000 <ip-address>
TIP: If you want to scan only the first 100 Ports then you can use the -F command as it fasts the process and only scans the first 100 Ports.
Detect OS and Versions
Well done! if you have come here, Let’s move on!
Detection of OS
Now we have to Detect which OS is running on the Host machine. In this part, the commands I will tell you may not work properly, but in the next part of Version Detection, there will be some different commands that will also tell you about the OS running. The reason for this, I will tell you later.
- -O
This command is used for Detecting the OS of the target machine but again it may not work properly, For this, there are two reasons,
First, It requires at least one open Port and one closed Port, So if you have not included any port that is open or closed then it will not give proper results, So make sure that you have included at least one open and one closed port.
Second, It guesses the OS running but does not give 100 percent accuracy. For example:
nmap -O -p 135,443 <ip-address>
TIP: As I have scanned ports earlier and I have the information that which ports are open and which are closed, So I included one open and one closed to get more accurate results try this technique.
Version Detection
To detect Versions of the running services and also OS detection one thing to keep in mind is that your machine and the target machine should establish a connection, I mean a Three-way handshake, So remember one thing not to use the Stealth scan command As it does not complete Three-way handshake.
- -sV (To detect Versions)
- — version-intensity <0–9> (0 being the lightest and 9 being the Highest and most accurate)
You can also use the -sV command alone but I recommend to use also — version-intensity 9 as 9 gives more accurate results, For example:
nmap -sV -p 135,443 <ip-address>
nmap -sV --version-intensity 9 -p 135,443,5039 <ip-address>
NOTE: It does not only give versions of the running services but also the OS running
Aggressive Scan
- -A
The Aggressive Scan gives a lot of information about the targeted machine with more accuracy and OS running, My favorite scan!
nmap -A -p 135 <ip-address>
Gives Information about:
- Services running on open ports
- Mac address
- OS running with high accuracy
- Network distance
- NetBIOS name
- Hop count
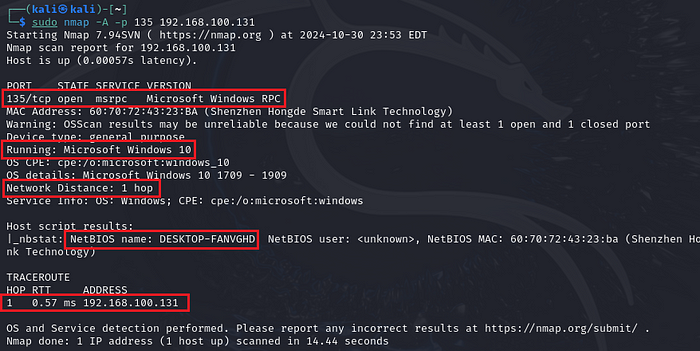
TIP: Make sure to include at least one open and one closed port.
Evasion Techniques and Spoofing
There are a lot of Evasion Techniques and spoofing yourself, Let’s learn First how to spoof yourselves!
1. Spoofing
There are a lot of spoofing techniques with their advantages and Disadvantages, by the way, I will tell you along the way the disadvantages of specific spoofing techniques.
Spoofing Mac Address
- — spoof-mac <write mac address manually> <Or enter the vendor name, i.e: dell>
For example:
nmap -sS --spoof-mac 42:53:53:63:62:B6 -p 45,62,73 <ip-address>
nmap -sS --spoof-mac dell -p 53,72,71 <ip-address>
Disadvantage: This only works for stealth scans or any other scan that does not complete a three-way handshake, scans that complete a three-way handshake might not work like version detection and scripting engine.
Decoy Scan
- -D RND: <number>
In the <number> option you can choose how many IP addresses you want, Decoy scan is used to scan the host but with different and random IP addresses and the number so specify, for example, if you enter 2 in <number> option and specify only one port then your IP and two more random IP will send packets to that only one port. For example:
nmap -sS -D RND: 4 -p 443,356 <ip-address>
Disadvantage: Same as spoofing Mac address, works great in Host discovery and port scanning phase but can’t work well in connection-oriented scans.
Spoofing Source port
- — source-port <port number>
simply spoofing your source port, only enter any number in the <port number> option. For example:
nmap -sS --source-port 53 -p 6432,256,135 <ip-address>
TIP: try to use 53, 20 as source ports for spoofing because DNS replies come from port 53 and active FTP from port 20, many administrators have fallen into the trap of simply allowing incoming traffic from those ports. They often assume that no attacker would notice and exploit such firewall holes.
2. Evasion Techniques
There are also a lot of evasion techniques, So let’s jump in!
Fragmentation:
- -f (fragment packets)
Fragmentation means dividing a Packets data into two parts, it can be used to bypass firewalls, For example:
nmap -sS -f -p 135 <ip-address>
MTU:
- — mtu <multiply of 8>
MTU means Maximum Transmission Unit, It should be 8 or multiply of 8, For example:
nmap -sS --mtu 16 -p 135 <ip-address>
TTL value:
- — ttl <any number>
Time to live is a field in packets used to identify the type of OS, you can change it by using simply this command, For example:
nmap -sS --ttl 64 -p 53 <ip-address>
Data length:
- — data-length <number>
Nmap only sends the packet with the header containing no data, By using this command we can insert random data (In Bytes) in the packet, For example:
nmap -sS --data-length 45 -p 135 <ip-address>
Conclusion
Nmap Advance Techniques can be used to bypass static firewalls, But it’s not always! I hope you have enjoyed the article! Good Luck!
