Set up Windows Server 2016 as a Domain Controller (DC)
Last updated: August 06, 2025
Setting up Windows Server 2016 as a Domain Controller (DC) requires two steps: installing the Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) role and promoting the server to a DC
Below, I will guide you through a step-by-step process on how you set up a Domain Controller in Windows Server 2016
What is an Active Directory?
Active Directory (AD) is a directory service developed by Microsoft that provides centralized control and management over users, computers, groups, and other resources within a network. It acts like a structured database that stores information about everything in a Windows network environment, including who can log in, what resources they can access, and what permissions they have.
AD is essential for organizations that need to manage a large number of users and devices securely and efficiently.
What is a Domain Controller?
A Domain Controller (DC), on the other hand, is a Windows Server that has been configured to run the Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) role. It is responsible for handling authentication requests, enforcing security policies, and maintaining the AD database.
Essentially, the Domain Controller is the server that makes Active Directory functional. It responds to login requests, verifies credentials, and ensures users have access to the right resources based on the rules defined in Active Directory.
Why do we need to set up Windows Server as a Domain Controller?
Setting up Windows Server as a Domain Controller is necessary because without it, the network cannot take advantage of Active Directory’s centralized identity and access management. In simple terms, the Domain Controller is what makes the AD environment work.
By promoting a server to a Domain Controller, you create the core of the domain-based network, which allows for consistent security policies, streamlined user management, and centralized control across all connected systems.
This setup is particularly crucial for enterprise environments, labs, or any situation where you want to simulate or manage multiple users and computers efficiently.
Step 1 – Installing the Active Directory Domain Services
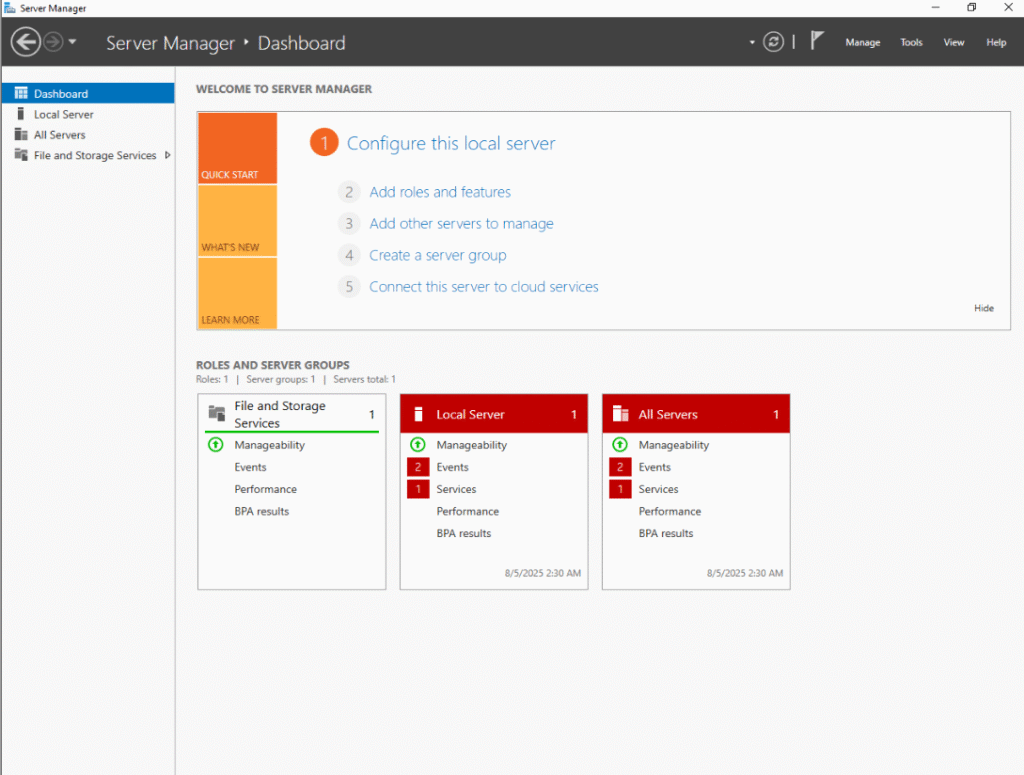
To install Active Directory Domain Services, in your Server Manager, go to -> Manage option -> then click on ‘Add Roles and Features‘
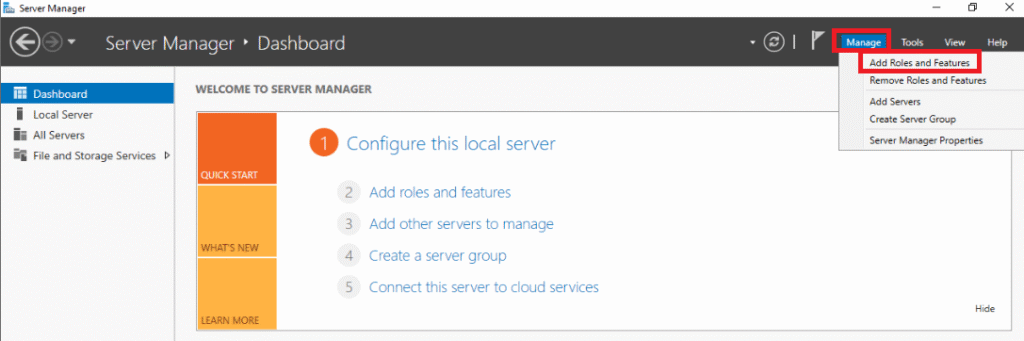
It will open the ‘Add Roles and Features Wizard‘
Simply Click Next
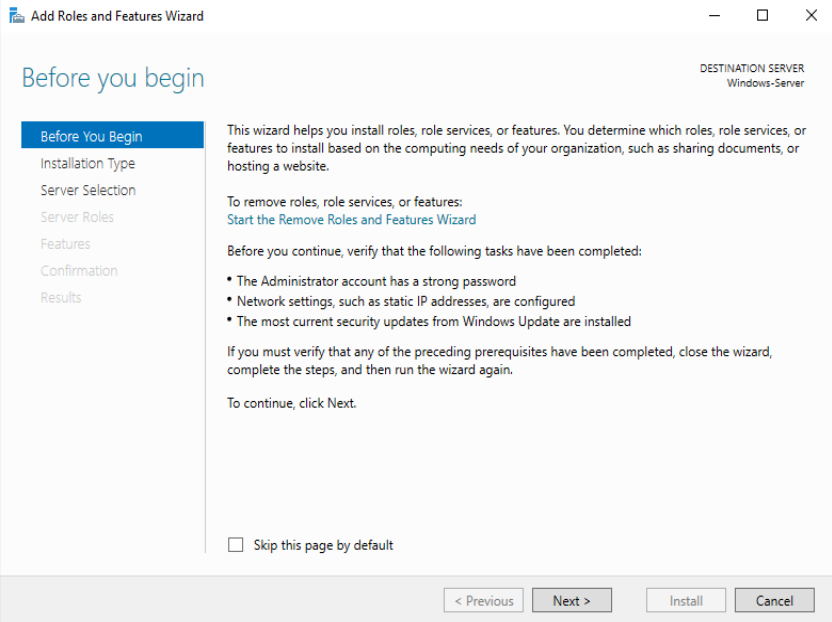
Select Role-Based installation and click Next
In Server Selection, Just check that it should show the Windows Server’s IP address!
Again click Next
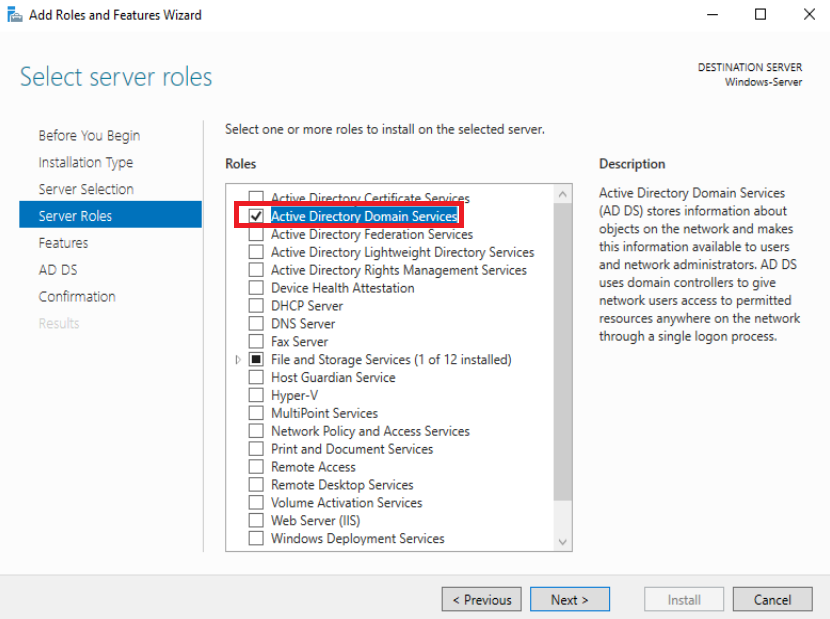
In Server Roles, you need to check the Active Directory Domain Services and click Next
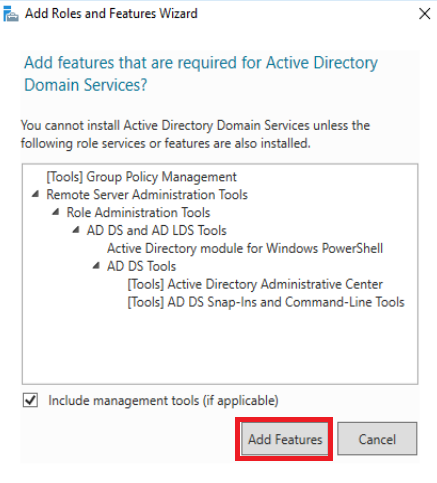
Just click on Add Features
Again, click on Next
And now just install
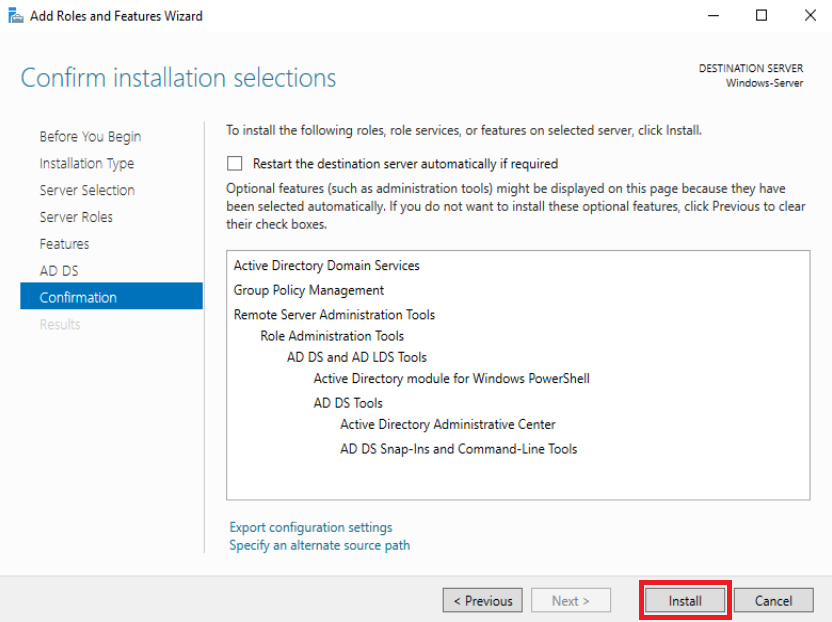
Once installed, in your dashboard, you can see the AD DS section on the left side
Now, the first step: Installing the Active Directory Domain Services has been completed
Step 2 – Promoting the Server to a Domain Controller
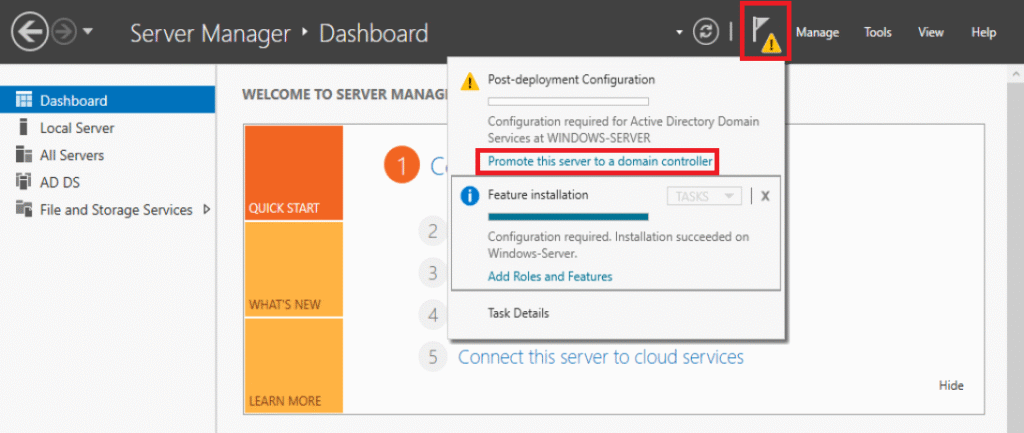
Now the second step is to promote the server to a domain controller, which is also a straight-forward method
Click on the Yellow triangle, then -> Promote this server to a domain controller
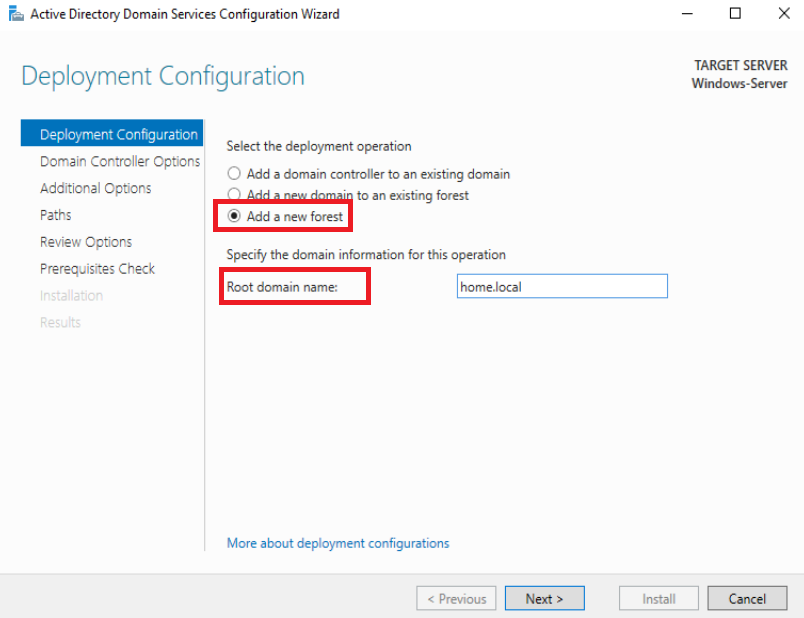
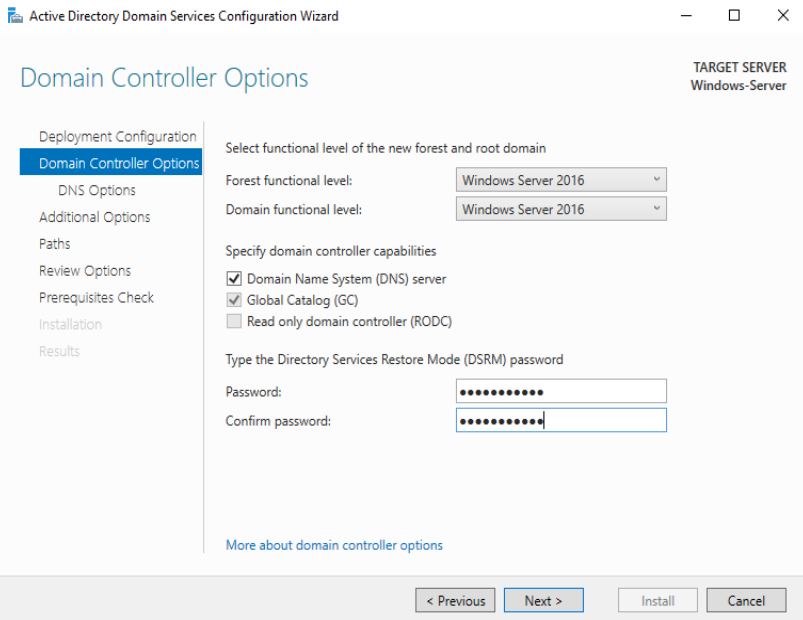
Click on ‘Add a new forest’ and set the Root domain name
Now just set up the password:
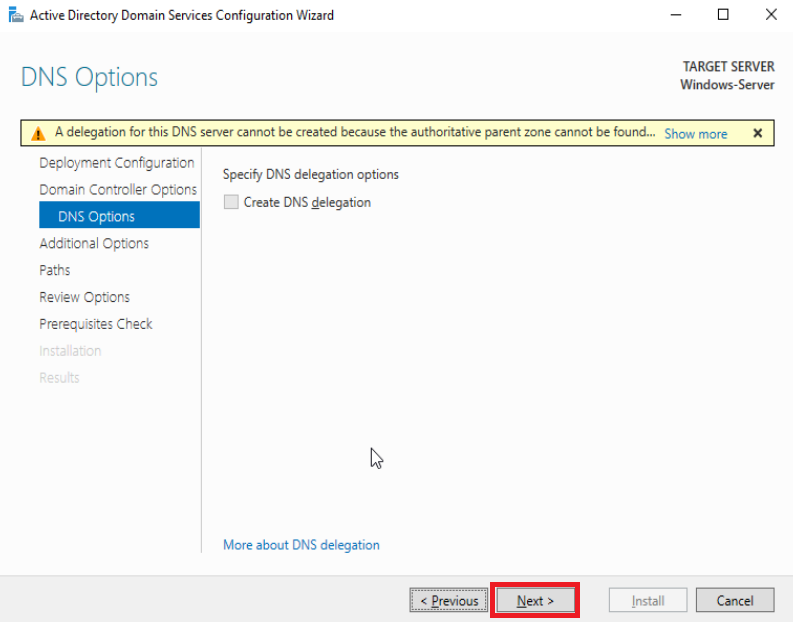
Ignore the DNS delegation option and hit Next
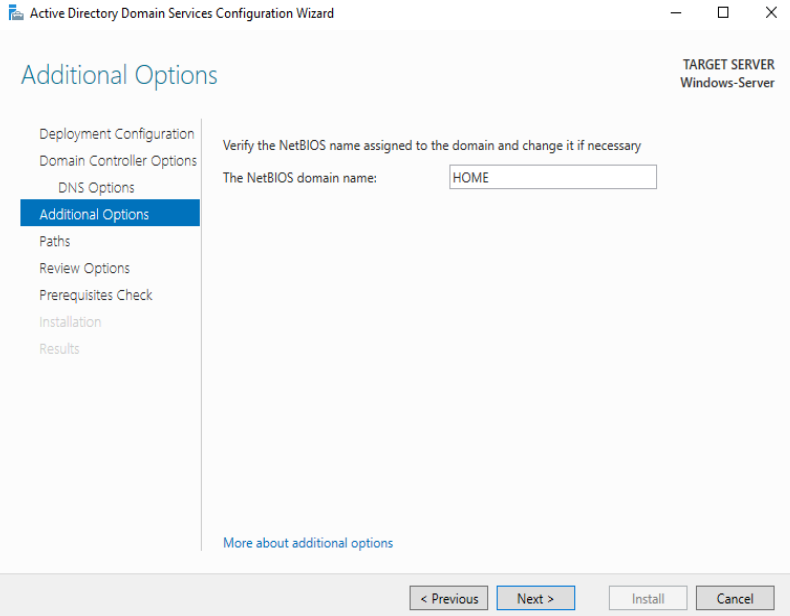
By default, the NetBIOS domain name will be set; leave it as it is:
Nothing Here, Next
Again Next
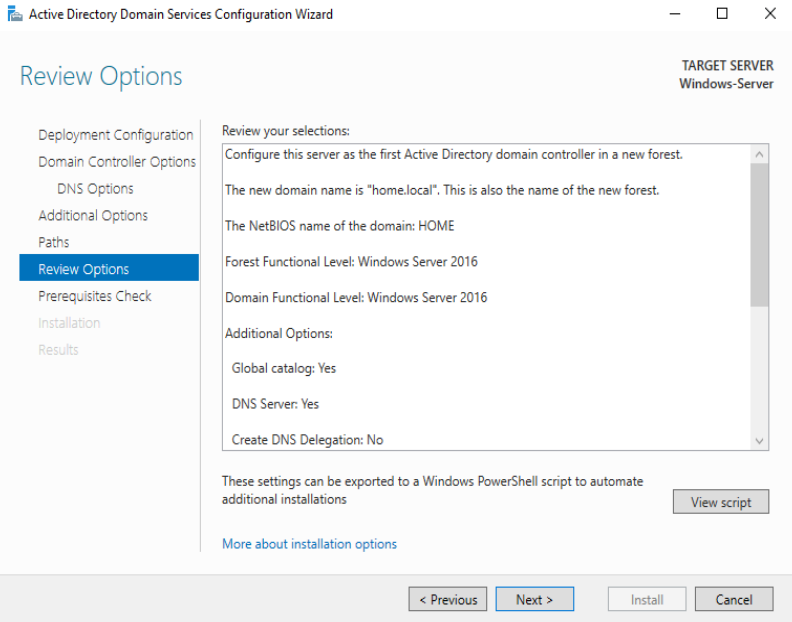
And Now Install it
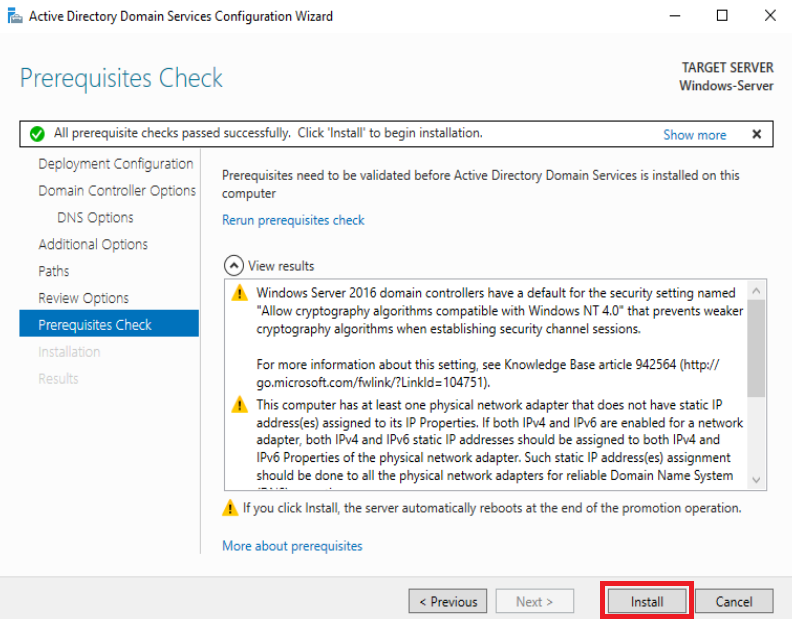
Once installed, your server is now configured as a Domain Controller. Below are some ways to verify it:
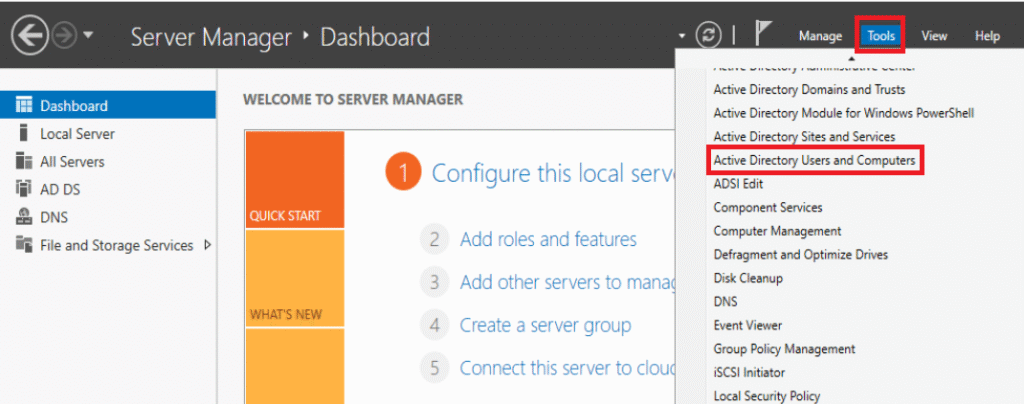
Verify through ADUC
Navigate to Tools -> Active Directory Users and Computers
You are now able to see your root domain name, and under it, there is the Domain Controller folder:
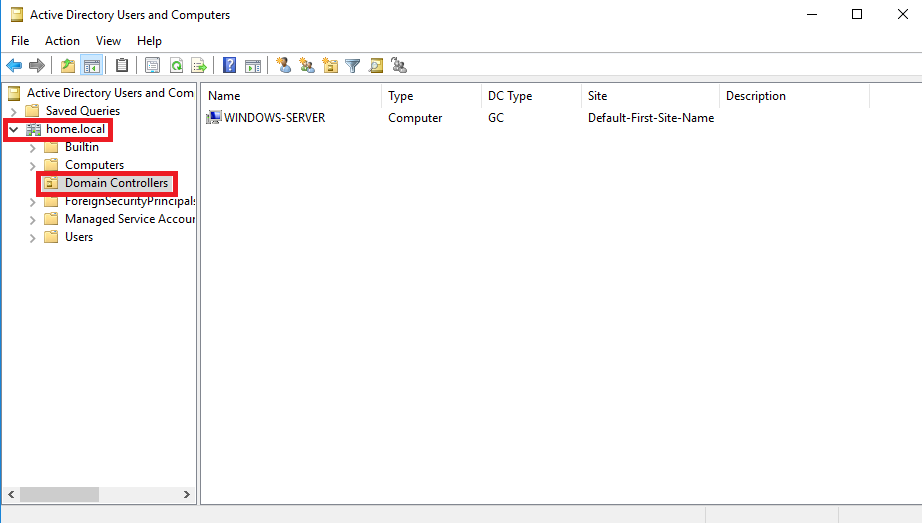
It shows all the Windows Servers that are part of the Domain Controllers. It means your Windows Server is successfully configured as a Domain Controller
Verify through DNS
Also, verify that LDAP, Kerberos services are properly configured in your Domain controller. For this, Navigate to your Dashboard:
Then: from your Dashboard -> Tools -> DNS
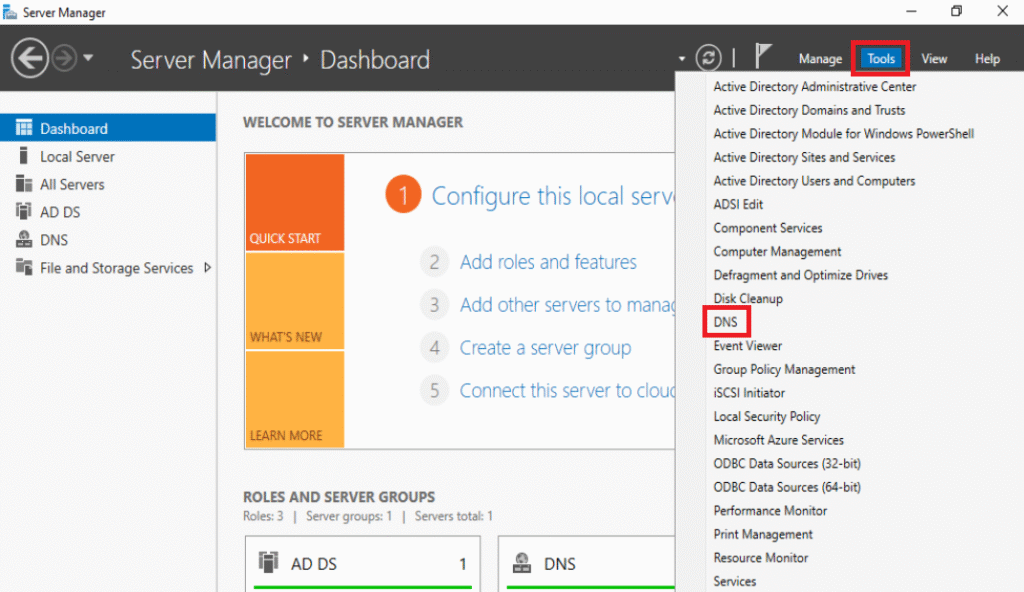
Under the Windows Server -> Forward Lookup Zones and you will find your root domain:
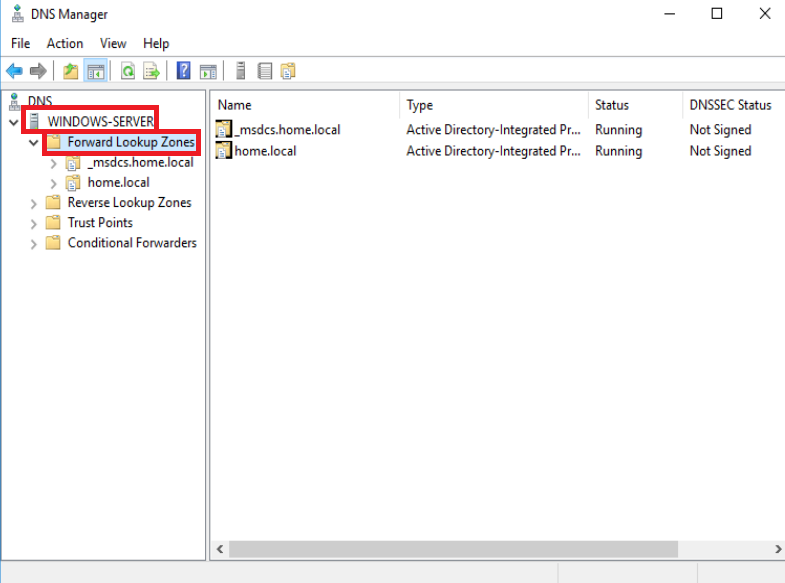
Then under your root domain -> _tcp folder -> verify that there is kerberos, ldap, etc
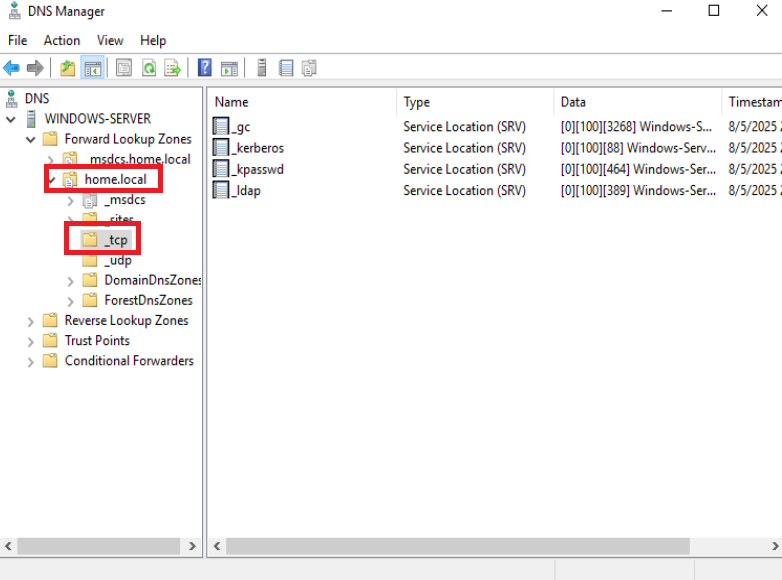
The Forward Lookup Zone for the domain contains critical records, including those in the _tcp subfolder, which hold SRV records like _ldap and _kerberos. These records enable clients to locate Domain Controllers for LDAP (directory queries) and Kerberos (authentication) services, which are fundamental to AD operations.
Checking these records ensures that AD services are discoverable, authentication works correctly, and the domain operates smoothly.
I hope you found this Article Helpful 🙂
