Chronohack – PicoCTF WriteUP | Reverse Engineering
Last updated: July 09, 2025
Hi! In this write-up, we will look at how to solve the Chronohack – Reverse Engineering Challenge in PicoCTF. So let’s dive in without wasting any time!
Description:
Can you guess the exact token and unlock the hidden flag? Our school relies on tokens to authenticate students. Unfortunately, someone leaked an important file for token generation. Guess the token to get the flag.
So we need to guess the token generated by the Python script. Download it and let’s analyze it:
import random
import time
def get_random(length):
alphabet = "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
random.seed(int(time.time() * 1000)) # seeding with current time
s = ""
for i in range(length):
s += random.choice(alphabet)
return s
def flag():
with open('/flag.txt', 'r') as picoCTF:
content = picoCTF.read()
print(content)
def main():
print("Welcome to the token generation challenge!")
print("Can you guess the token?")
token_length = 20 # the token length
token = get_random(token_length)
try:
n=0
while n < 50:
user_guess = input("\nEnter your guess for the token (or exit):").strip()
n+=1
if user_guess == "exit":
print("Exiting the program...")
break
if user_guess == token:
print("Congratulations! You found the correct token.")
flag()
break
else:
print("Sorry, your token does not match. Try again!")
if n == 50:
print("\nYou exhausted your attempts, Bye!")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\nKeyboard interrupt detected. Exiting the program...")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
What’s it doing?
token_length = 20
The token length is 20 letters, which means we have to enter a token of 20 letters in length, and then it passes to the “get_random” function.
The token contains numbers and letters only!
alphabet = "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
Then it seeds it with the current time in milliseconds (Unix epoch time)
random.seed(int(time.time() * 1000))
Then the “random.choice” method returns a randomly selected element from the specified string.
The Time is based on the Unix epoch time, so the seed generated depends on the current time.
So,
Practically, it is not possible that we guess the token (which is random and 20 letters long) at the same time interval, as network latency is also an issue. So, to solve this, below is the Python script for it that will brute-force it and will add +1 ms offset, as we have 50 attempts. After 50 attempts, it will reinitiate the connection and start it where it left it.
Solution Approach
The token is generated when the server accepts our connection, so we need to estimate the server’s time (Ts) and test seeds around it. The steps are:
- Connect to the Server: Use a socket to connect and receive the welcome message.
- Estimate Server Time: Record the local time when the welcome message is received (T_welcome) and adjust for network latency using a dummy guess to measure round-trip time (RTT).
- Generate Tokens: Create tokens for seeds in a range (e.g., Ts — 50 ms to Ts + 1000 ms) to account for timing differences.
- Handle Attempt Limits: If 50 attempts are exhausted, reconnect and continue testing remaining seeds.
- Stop on Success: Exit immediately when the correct token is found, retrieving the flag.
Here is the Python Script:
NOTE: Change the PORT value to your connection given in the challenge
import socket
import time
import random
import sys
def get_random(length, seed):
"""Generate a random token with the given seed and length."""
alphabet = "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
random.seed(seed)
return ''.join(random.choice(alphabet) for _ in range(length))
def connect_and_guess(start_seed_index, seeds, offsets, Ts, host, port, token_length, max_attempts):
"""Connect to the server and attempt to guess the token starting from start_seed_index."""
client_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
try:
client_socket.connect((host, port))
print(f"Connected to {host}:{port}")
response = client_socket.recv(4096).decode("utf-8")
print("Server response:")
print(response)
T_welcome = int(time.time() * 1000)
if start_seed_index == 0:
dummy_guess = "dummy"
T_send = int(time.time() * 1000)
client_socket.send((dummy_guess + "\n").encode("utf-8"))
reply = client_socket.recv(4096).decode("utf-8")
T_receive = int(time.time() * 1000)
print("Dummy guess reply:")
print(reply)
RTT = T_receive - T_send
one_way_delay = RTT / 2
Ts[0] = T_welcome - one_way_delay
print(f"Estimated Ts: {Ts[0]}, RTT: {RTT}, Delay: {one_way_delay}")
else:
Ts[0] = T_welcome
print(f"Reconnection Ts: {Ts[0]}")
print(f"Testing seeds around Ts={Ts[0]} ms")
print(f"Total seeds to try: {len(seeds)}")
print(f"Starting at offset: {offsets[start_seed_index]} ms")
print(f"Starting at seed: {seeds[start_seed_index]}")
attempts_made = 0
for i in range(start_seed_index, len(seeds)):
if attempts_made >= max_attempts - (1 if start_seed_index == 0 else 0):
print("Reached 50 attempt limit. Will reconnect.")
return i
seed = seeds[i]
offset = offsets[i]
guess = get_random(token_length, seed)
print(f"Attempt {attempts_made + 1}: Trying {guess} (Offset: {offset} ms)")
client_socket.send((guess + "\n").encode("utf-8"))
reply = client_socket.recv(4096).decode("utf-8")
print("Server reply:")
print(reply)
attempts_made += 1
if "Congratulations" in reply or "flag" in reply.lower():
print("Success! The correct token was:", guess)
client_socket.close()
print("Connection closed")
sys.exit(0)
return len(seeds)
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred: {e}")
return start_seed_index
finally:
client_socket.close()
print("Connection closed")
def main():
# Server details
HOST = "verbal-sleep.picoctf.net"
PORT = 52069 #Change the port HERE
token_length = 20
max_attempts = 50
range_start_ms = -50 # Start at Ts - 50 ms
range_end_ms = 1000 # End at Ts + 1000 ms
Ts = [0]
offsets = list(range(range_start_ms, range_end_ms + 1))
seeds = [0] * len(offsets)
print(f"Total seeds to try: {len(seeds)}")
start_seed_index = 0
while start_seed_index < len(seeds):
client_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
try:
client_socket.connect((HOST, PORT))
response = client_socket.recv(4096).decode("utf-8")
T_welcome = int(time.time() * 1000)
client_socket.close()
Ts[0] = T_welcome
seeds = [int(T_welcome + offset) for offset in offsets]
print(f"Initial Ts for connection: {Ts[0]}")
result = connect_and_guess(start_seed_index, seeds, offsets, Ts, HOST, PORT, token_length, max_attempts)
if result == -1:
break
start_seed_index = result
if start_seed_index < len(seeds):
print(f"Reinitiating connection to try seeds starting from index {start_seed_index} (Offset: {offsets[start_seed_index]} ms)")
time.sleep(1)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Connection error: {e}")
time.sleep(1)
if start_seed_index >= len(seeds):
print("Exhausted all seeds without finding the correct token.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
As it will depend on the Network Latency to guess the correct token based on the Unix epoch time on the Server,
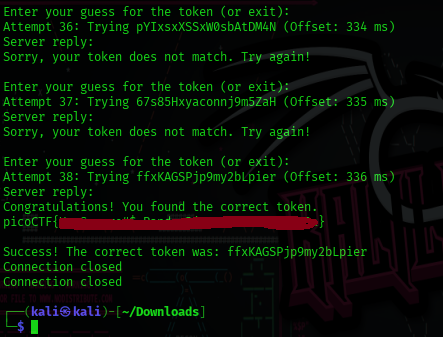
Mine worked at 336ms, so don’t worry! As it finds the flag, it will stop.
Thanks for Reading 🙂
